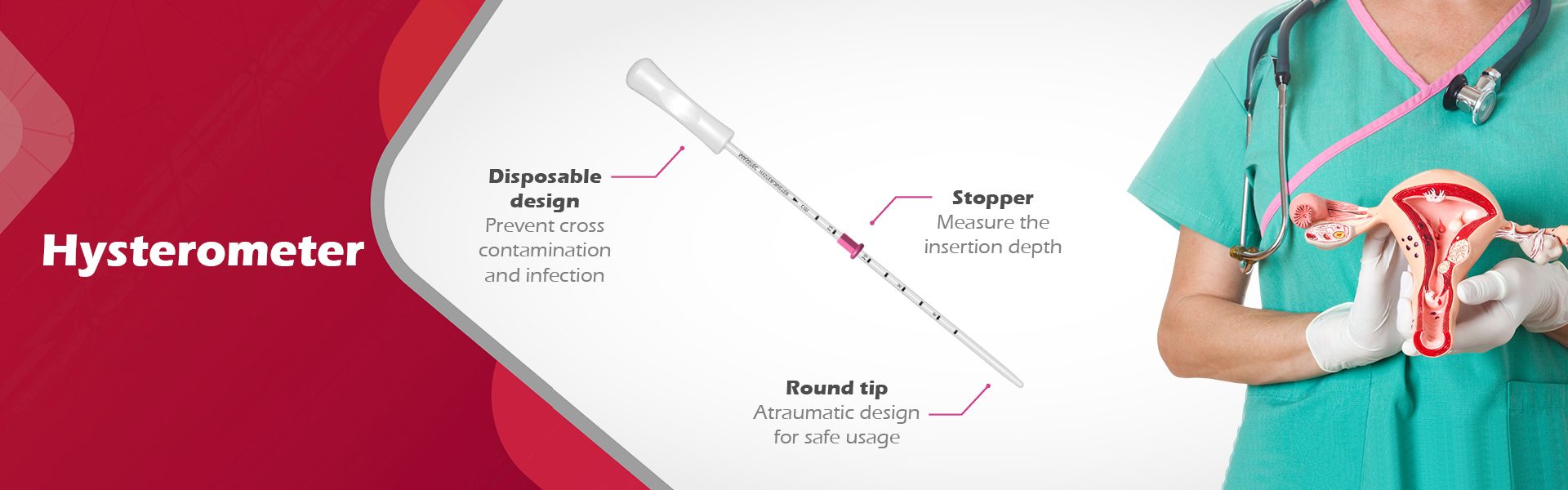
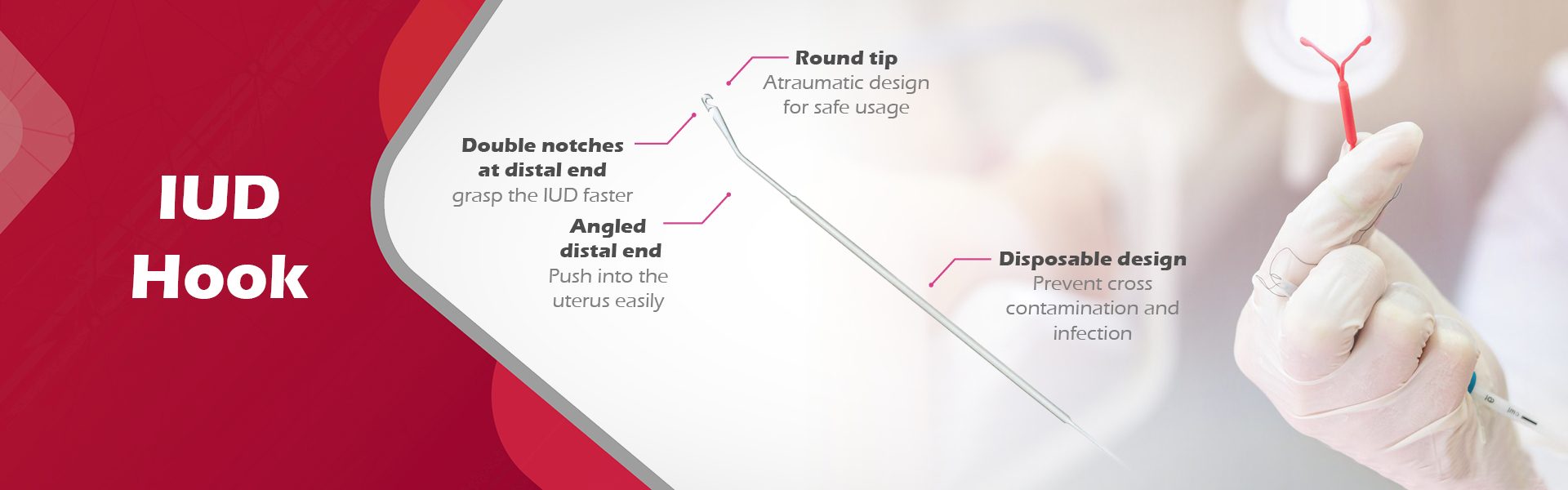
Menu
Close
- Home
- About
- Products
GASTROENTEROLOGY

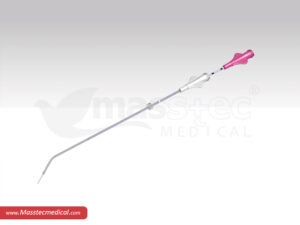
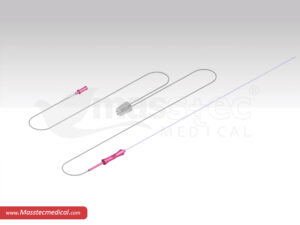
BIOPSY NEEDLES

SURGERY

- News
- Contact
- Home
- About
- Products
GASTROENTEROLOGY

BIOPSY NEEDLES

SURGERY

- News
- Contact
- Home
- About
- Products
GASTROENTEROLOGY

BIOPSY NEEDLES

SURGERY

- News
- Contact
- Home
- About
- Products
GASTROENTEROLOGY

BIOPSY NEEDLES

SURGERY

- News
- Contact
Menu